China’s Surgical Robots Revolutionize Healthcare with AI Precision
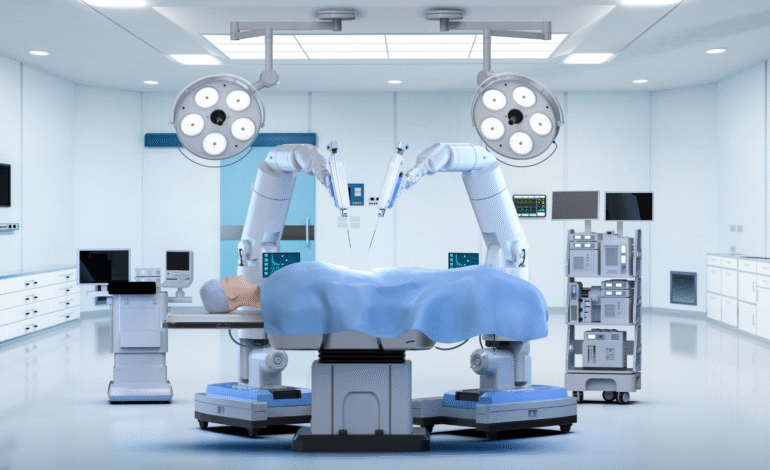
China’s technological advancements have become a global talking point, and among the most groundbreaking developments is the integration of artificial intelligence-powered robots into the medical field. While robots have long been present in industrial manufacturing and logistics, their entry into the domain of complex surgeries marks a major shift in healthcare. In hospitals across the country, these robotic systems are now being trusted with life-saving procedures, enhancing precision, reducing human error, and significantly improving recovery times.
This transformation is not just about technological sophistication; it reflects a changing medical landscape in which machine-assisted operations are becoming a norm rather than a novelty. This article explores how China’s rapidly growing robotics industry is redefining surgical practices, the scope of AI integration, and what it means for global medical innovation.
China’s Rise as a Robotics Innovation Powerhouse
Over the past decade, China has risen from being a consumer of robotic technology to one of its foremost innovators and manufacturers. According to reports from China Central Television (CCTV), the nation’s robotics sector has enjoyed extensive support from the government through policy incentives, research funding, and public-private partnerships. These efforts have led to the creation of sophisticated robotic systems designed not only for industrial use but also for sectors such as education, logistics, agriculture, and notably, healthcare.
The healthcare-focused robots emerging from China are equipped with advanced artificial intelligence, computer vision, and machine learning capabilities. These technologies enable them to assist in surgeries with enhanced accuracy, adapt to real-time changes during operations, and learn from prior procedures to improve outcomes.
Surgical Robotics in Practice: Speed and Precision
The real test of robotic efficiency in medicine lies in the operating room. At the Third Affiliated Hospital of Southern Medical University in Guangzhou, Dr. Fan Shicai leads a team that works closely with surgical robots. According to Dr. Fan, orthopedic surgeries that used to take five hours now take merely thirty minutes. The robots are designed to replicate and even surpass human precision, particularly in procedures that require microscopic accuracy and steady hands over extended periods.
This ability to significantly cut down surgery times means patients spend less time under anesthesia, which reduces the risk of complications. It also translates to quicker recoveries, shorter hospital stays, and ultimately, reduced costs for both hospitals and patients.
Medical Robotics: From Assistance to Autonomy
Currently, surgical robots function mostly as highly advanced tools that assist doctors. The surgeon remains in control, using the robot to make precise incisions, navigate delicate anatomical structures, or perform repetitive actions with unwavering accuracy. However, developments are ongoing that will allow these machines to take on more autonomous roles, particularly in diagnostics, pre-surgery mapping, and even decision-making during operations.
China’s AI researchers are exploring models where robotic systems can detect issues such as abnormal tissue growth or internal bleeding faster than traditional methods. By integrating AI algorithms with real-time data collection, surgical robots could in the future provide instant feedback and risk assessments mid-surgery.
Impact on Rural Healthcare and Accessibility
One of the most promising aspects of medical robotics is the potential to extend high-quality surgical care to rural and underserved areas. In China, vast distances and uneven healthcare infrastructure often mean that patients in remote regions do not receive timely medical attention. With the help of remote surgery systems and telemedicine platforms powered by 5G and AI, a surgeon in Beijing could theoretically operate on a patient hundreds of miles away using a robotic interface.
This shift could democratize access to healthcare, bridging the urban-rural divide and allowing more people to benefit from advanced medical procedures. While challenges remain — including reliable internet infrastructure and training for local medical staff — the groundwork for such a transformation is already being laid.
Education and Training Through Robotic Simulation
China’s commitment to robotics also extends to the education and training of new surgeons. Medical schools and hospitals are increasingly adopting robotic simulators that replicate real surgical environments. These platforms offer aspiring doctors the opportunity to practice intricate procedures without the risk of harming a patient.
Using haptic feedback, 3D imaging, and real-time data analytics, these simulators help students gain confidence and skill before they step into an actual operating room. It is an investment not only in technology but in building a new generation of highly skilled, tech-savvy surgeons who can work in harmony with machines.
Addressing Ethical and Regulatory Challenges
The rapid integration of AI-powered robots into surgery also raises questions about ethics and regulation. Who is responsible if a robotic system fails mid-surgery? How do you ensure patient data privacy when AI algorithms are involved? What kind of consent is needed when robots assist in life-critical procedures?
China, like many other countries pioneering robotic medicine, is in the process of developing regulatory frameworks that address these concerns. Medical institutions, legal experts, and government agencies are working together to create guidelines that ensure safety, transparency, and accountability. The goal is to protect patients while enabling innovation to flourish.
Global Implications of China’s Robotics Advancements
China’s emergence as a leader in medical robotics is likely to influence global trends. As these technologies become more refined and cost-effective, other countries may adopt similar systems, transforming their own healthcare practices. Already, Chinese companies are expanding their reach, offering robotic solutions to international hospitals and research institutions.
Collaboration between nations on robotic surgery technologies can pave the way for standardized systems, shared medical data (with patient privacy protections), and collaborative research in rare disease treatment, advanced diagnostics, and AI-assisted rehabilitation therapies.
Future Outlook: A Partnership Between Human and Machine
Looking ahead, it is unlikely that robots will completely replace human surgeons. Instead, the future of medicine seems to be headed toward collaboration — a synergy between human intuition and mechanical precision. Surgeons will increasingly rely on robots for the execution of delicate tasks while focusing their own expertise on diagnosis, decision-making, and patient interaction.
This hybrid model promises not only better outcomes but also a more humane and thoughtful approach to surgery. As AI continues to evolve, it may take on more responsibilities, but the role of the physician remains indispensable in guiding, supervising, and connecting with the patient.
Technology’s Healing Touch in Modern Healthcare
China’s advancements in AI robotics and their application in surgical procedures symbolize a monumental shift in how healthcare is delivered. From shortening operation times and improving surgical outcomes to offering hope for remote communities, these robots are proving to be more than just mechanical tools — they are redefining what is possible in modern medicine.
While challenges regarding ethics, regulation, and infrastructure remain, the trajectory is clear: robotic technology will play a central role in the future of surgery not just in China, but across the world. And as this integration continues, what once seemed like science fiction becomes a new standard of care — a future where human skill and robotic precision save lives together.







