SpaceX Starship Flight 10 Success Brings Mars Dream Much Closer
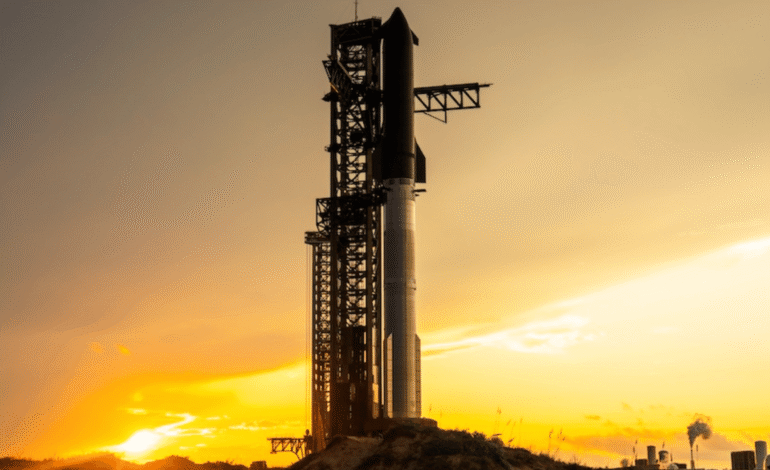
On August 26, 2025, SpaceX celebrated a major achievement. The company completed the tenth test flight of its Starship rocket. The launch took place from Starbase in Texas. After flying in space, the rocket splashed down in the Indian Ocean about an hour later.
The test had already been delayed twice. First, engineers found a problem in the ground system. Next, bad weather forced another postponement. Still, when the rocket finally lifted off, it showed the world that hard work and persistence pay off.
This was more than a test. It was a step toward a future where humans can travel to the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
What Is Starship and Why It Matters
The Starship system has two parts: the Super Heavy booster and the Starship spacecraft. Together, they form the tallest and most powerful rocket ever built. At more than 120 meters high, it is taller than many skyscrapers.
Starship is designed to be fully reusable. That means both parts the booster and the spacecraft should return safely after each flight so they can fly again. This idea could change space travel forever. Instead of throwing away rockets after one mission, Starship could fly like an airplane, reducing the cost of space launches.
The big dream behind Starship is simple: make life multiplanetary. Elon Musk and his team at SpaceX believe humans should live on more than one planet. With Starship, they want to make travel to the Moon, Mars, and even farther destinations possible.
A History of Failures Before Success
Getting to this point was not easy. Many earlier flights ended in failure. Some rockets exploded during launch. Others failed to land correctly. Flights seven, eight, and nine were especially difficult.
But SpaceX has a unique way of looking at failure. Each crash was seen as a chance to learn and improve. Musk often said, “Every failure brings us closer to success.”
This strategy worked. By Flight 10, the company had enough lessons to make the rocket perform better than ever before.
The Launch That Made Headlines
After the delays, the rocket finally launched on Tuesday evening, August 26. At 6:30 p.m. Central Time, the countdown ended and all 33 Raptor engines on the Super Heavy booster fired. The rocket lifted off with a force stronger than any other vehicle in history.
The booster and the Starship spacecraft separated smoothly. The booster returned toward the Gulf of Mexico for a controlled splashdown. To test safety systems, engineers even shut down one engine early. The booster handled the situation well, showing the rocket’s ability to survive problems in flight.
Meanwhile, Starship itself continued into space. It carried a mock payload of satellites and showed that it could handle all stages of the mission.
What Flight 10 Achieved for the First Time
Flight 10 marked many firsts in the Starship program:
Payload deployment: For the first time, Starship released satellite simulators in orbit. This shows it can be used to launch Starlink satellites and other payloads.
Engine restart in space: Engineers restarted one of the Raptor engines while Starship was in orbit. This test proved the rocket can maneuver in space, which is vital for long missions.
Heat shield test: On its way back, Starship faced extreme heat. Some of its heat-shield tiles melted, but the rocket survived long enough to show the system works.
Controlled splashdowns: Both the booster and the spacecraft reached the ocean in controlled descents. The booster splashed in the Gulf of Mexico. Starship landed in the Indian Ocean, breaking apart on impact as expected.
Each of these milestones shows Starship is moving closer to becoming fully operational.
Why This Flight Matters for the World
This success is not just important for SpaceX. It has global impact:
- For NASA and the U.S.: Starship is part of NASA’s Artemis program, which will send astronauts back to the Moon. NASA has chosen Starship as a lunar lander.
- For Mars missions: A rocket this powerful is needed to send humans and equipment to Mars. Flight 10 is a step closer to that goal.
- For global business: If Starship can launch satellites cheaply, internet projects like Starlink will grow faster. Other companies can also use it to launch satellites at lower cost.
- For space tourism: In the future, Starship may carry people for short trips to space.
The UAE and Middle East: Inspired by SpaceX
In the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and across the Middle East, interest in space is growing fast. The UAE has already launched the Hope Probe to Mars, built satellites, and sent astronauts to the International Space Station. Projects like the Rashid rover show that the UAE is serious about the Moon as well.
For this region, SpaceX’s success is inspiring. It shows what is possible when vision meets technology. The UAE could also benefit directly. Reusable rockets like Starship may reduce launch costs, making it easier for universities, startups, and government projects in the Middle East to send payloads into space.
The Mohammed Bin Rashid Space Centre (MBRSC) has already proved the UAE can compete on a global level. With partnerships and collaborations, the UAE could take part in missions that go far beyond Earth.
Benefits Beyond Space Exploration
The success of Starship will affect more than just astronauts and scientists.
Lower launch costs: If Starship becomes reusable, it will make space cheaper. This helps research, weather monitoring, and even agriculture through better satellites.
Scientific progress: More launches mean more experiments. Medicine, materials, and climate studies can all benefit.
Tourism and education: Space tourism could become real in the coming years. Countries like the UAE could attract visitors by becoming hubs for training or space travel.
Youth inspiration: Every big achievement in space inspires students to study science and engineering. This is already happening in the UAE, and Starship adds more excitement.
Challenges That Remain for SpaceX
While Flight 10 was a success, there are still challenges ahead:
Reusability: SpaceX must show both the booster and Starship can land safely and fly again many times.
In-space refueling: For long missions to Mars, the rocket will need to refuel in orbit. This has not been tested yet.
Human safety: Carrying people requires a higher safety standard than carrying satellites.
Regular flights: SpaceX will need to launch Starship again and again, reliably, before it can become a trusted workhorse.
The Road Ahead
SpaceX will continue testing Starship with more flights planned for late 2025 and beyond. Each test will improve the design and bring the rocket closer to regular use.
NASA is preparing to use Starship for its Artemis III mission to the Moon, expected around 2027. Longer-term, the company aims for cargo and even crewed missions to Mars.
For the UAE and Middle East, the future is exciting. The region is already investing in space and science. Partnering with global leaders like SpaceX could put the UAE in a leading role in the coming space age.
A Shared Human Dream
The tenth Starship flight is a turning point in modern space history. With successful payload deployment, engine restart, heat shield testing, and controlled splashdowns, SpaceX has shown that its vision is working.
This was not just about one company or one country. It was about a shared human dream to go farther, explore more, and make life beyond Earth possible.
For SpaceX, it is a victory after years of hard work. For the world, it is a sign that a new space era is beginning. And for the UAE and the Middle East, it is inspiration to keep building, innovating, and dreaming big.
The stars are no longer far away. Flight 10 has brought them a little closer.







